Mon, 11 May 2020
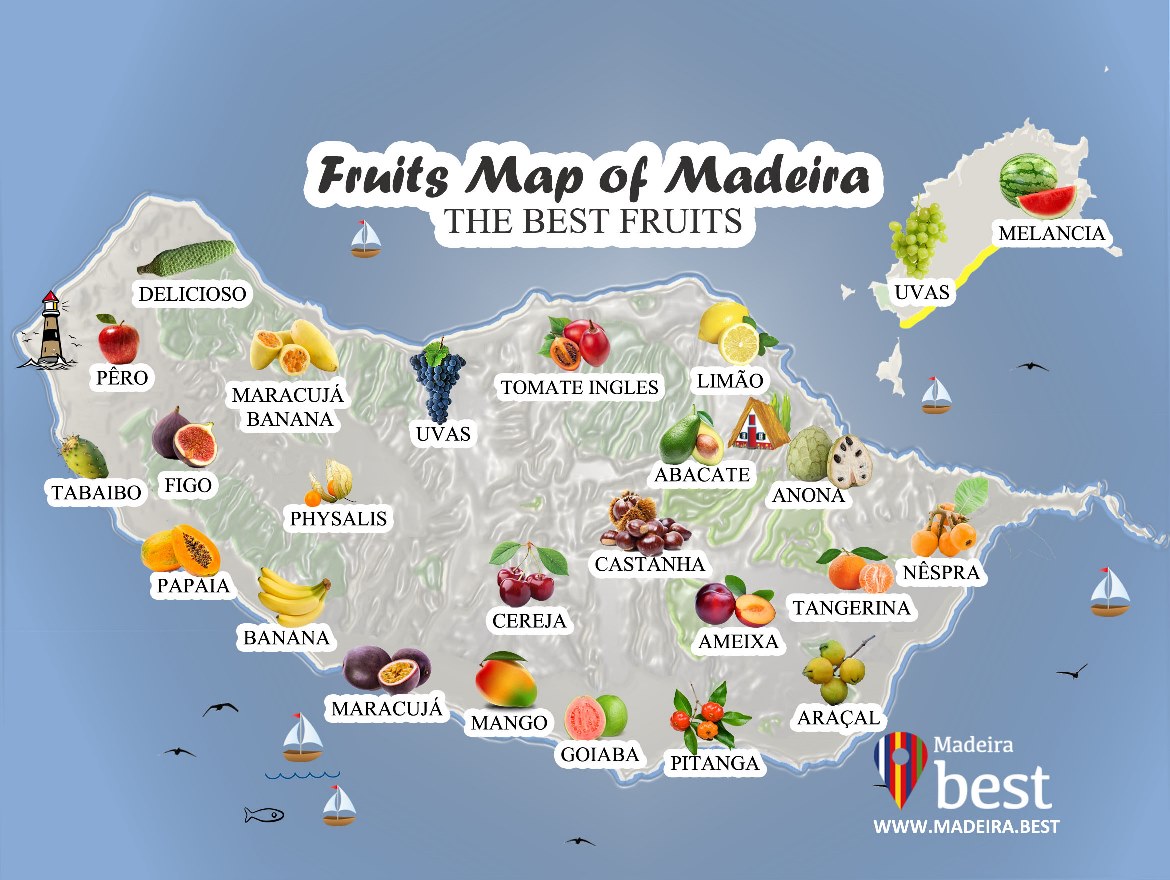
25 Fruits of Madeira Island
The varied fruits that we can find both on Madeira Island and Porto Santo are just some examples of the uniqueness of the Islands of Madeira and Porto Santo.
So let's look at some of the most famous examples and where we can find them!
Anona or Custard Apple
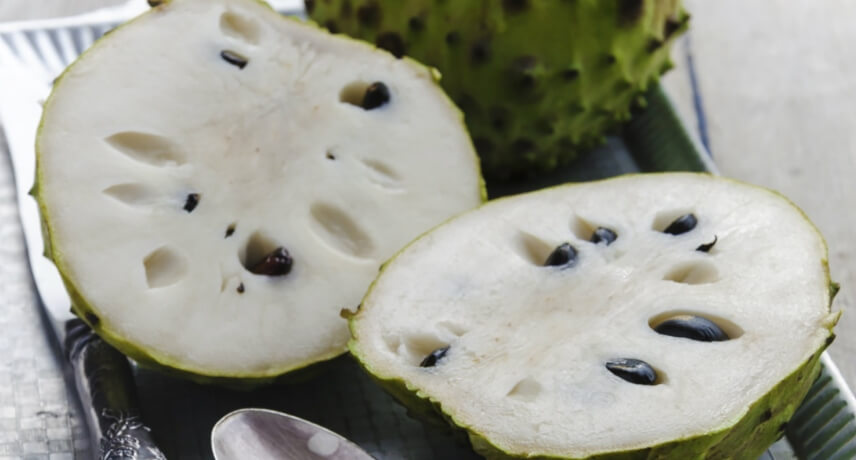

Anona is a fruit from the Andes. This fruit was introduced in Madeira in the 17th century, brought by merchants from South America.
This fruit immediately showed a good adaptation to the climatic conditions of the region, and nowadays, the anoneira orchards are between 280m to 550m above sea level.
Modern production is concentrated in the municipality of Santana (Faial in particular), and there are also some orchards in the area of Machico, Santa Cruz and Funchal (albeit in lesser quantities).
Anona, whose scientific name is Anona cherimolia Mill, is a fruit typically sweet and delicate to the touch, having a particularly high energy value, around 75kcal per 100g. It is common to find large and heavy anonas, which makes them a perfect fruit to share! It can be eaten at room temperature or refrigerated (not for long, otherwise the anona's skin starts to brown and oxidize), this last option is perfect for those who want a refreshing dessert, but healthier than your typical ice cream.
The fruit is rich in simple and complex carbohydrates, Vitamin C (very important for its antioxidant action and for the maintenance of collagen in the skin and muscles), Vitamin B6 (present in metabolic processes such as the production of antibodies, also contributing to the reduction of fatigue), potassium (contributes to the natural processes of elimination of toxins), iron (imperative for hemoglobin and oxygen transportation in the blood), fibers (which help in intestinal health, namely in maintaining a healthy intestinal flora) and other elements with anti-inflammatory properties.
Guava
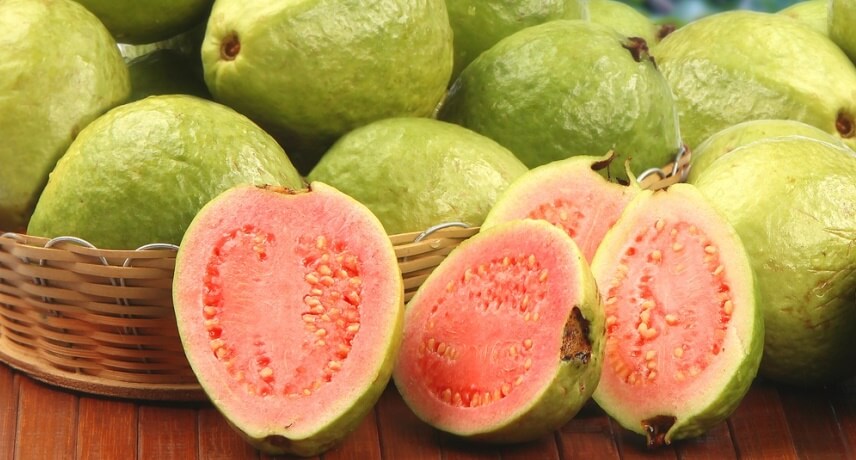

Guava (scientific name Psidium pyriferum) is another tropical fruit originating in the Americas. It is a fruit stuffed with seeds, with a light and sweet taste, with an interior usually pink and a relatively low in energy value (about 68 kcal per 100g).
Guava trees usually bear fruit in the autumn / winter season, between October and February. Its production is mainly done on the south coast of the island, mainly in the municipalities of Funchal, Câmara de Lobos and Ribeira Brava.
Guava is rich in fiber, contributing to the maintenance of good intestinal transit, so it helps with digestion. This tropical fruit is abundant in antioxidants, such as lycopene and vitamin C. These help to prevent the aging of cells, as they avoid the damage caused by free radicals. The presence of vitamin C also enhances the absorption of iron by the body, which is why it is recommended for people suffering from anemia.
In Madeira it is common for guava to be used in jams, smoothies, juices and even liquor.
Pitanga
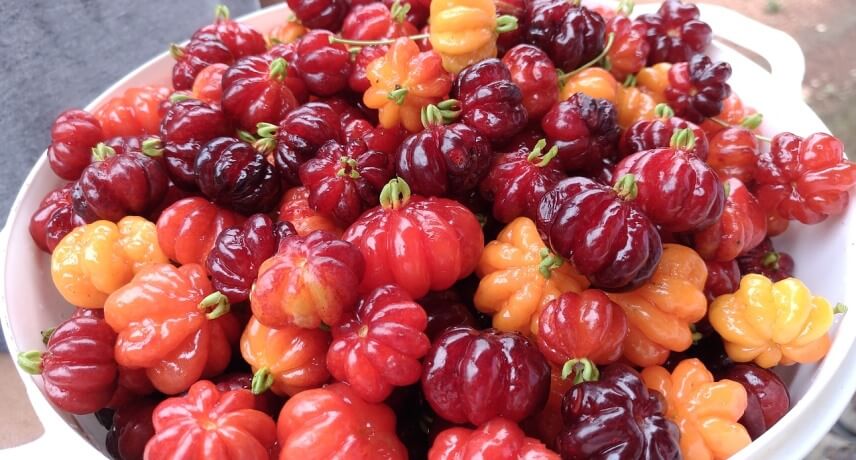

The pitanga, Eugenia uniflora L., is another tropical fruit coming directly from Brazil to Madeira Island. It is not a very likely fruit to be commercialized, since from the moment it ripens it is extremely delicate and easily spoils, which makes its storage and transportation not economically viable. These factors make it a fruit unknown to many Portuguese and foreigners who visit us (with the notable exception of Brazilians).
The trees, the pitangueiras, germinate easily, to the point of being used in public spaces and gardens and bearing fruit several times a year. Most are on the south coast of the island, between Funchal and Ponta do Sol.
Pitanga has a bittersweet flavor: if harvested with an orange to red colour, it is more acidic, while harvested with a dark red or even almost black tone, it is much sweeter. This versatility makes it used in different ways in cooking, from jams and chutneys to traditional alcoholic beverages such as poncha.
In nutritional terms, it is a fruit low in sugar, with the presence of vitamin A, an important element for vision and the immune system (it stimulates the production and activity of white blood cells). It is also rich in vitamin C.
Passion fruit
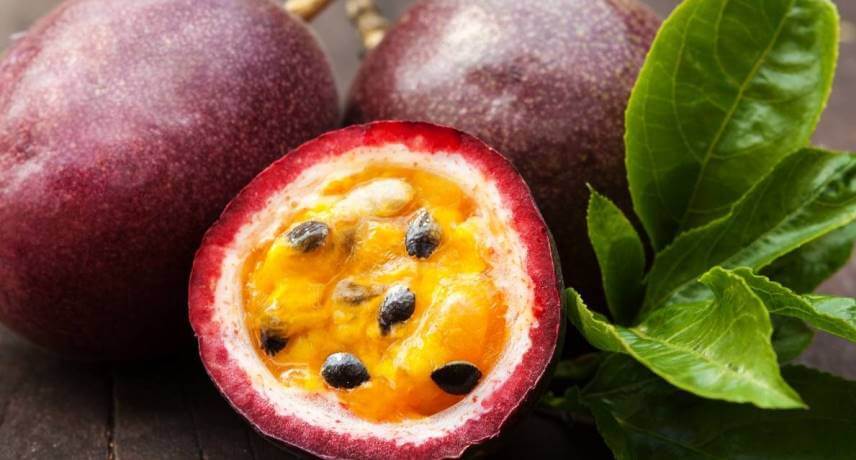

Few fruits are as associated with Madeira as passion fruit (with the exception perhaps of the banana mentioned later), however it came from Brazil. Passion fruit is a small, round fruit with a gelatinous pulp rich in seeds. It comes from passion fruit tree, a fast-growing climbing plant. In Madeira there are essentially 3 varieties, the regional purple (Passiflora edulis Sims .: Passiflora edulis f. Sp. Edulis), the Brazilian yellow (Passiflora edulis f. Sp. Flavicarpa) and an F1 hybrid. The most consumed and known is the purple, which has an intense and slightly acidic flavor.
Passion fruit plants are somewhat temperamental plants, sensitive to wind, excess and lack of water. It is a tropical fruit par excellence and found fertile soils in excellent conditions in Madeira Island. it is produced mainly in the municipalities of Machico, Santa Cruz, Ribeira Brava, Ponta do Sol and Calheta.
Passion fruit is widely used in Madeiran gastronomy, in traditional poncha, in jams, chutneys, in sauces to be used with fish, in liqueurs, ice creams and other sweets. It is also common to eat natural passion fruit or add a little sugar to the pulp and eat it as a dessert!
Passion fruit is rich in B vitamins, calcium, iron, phosphorus, sodium and potassium. It is said to have soothing and antioxidant properties, which help to combat aging and cell degeneration. The oil that can be extracted from passion fruit also has important cosmetic applications, acting as an emollient for the skin.
Banana
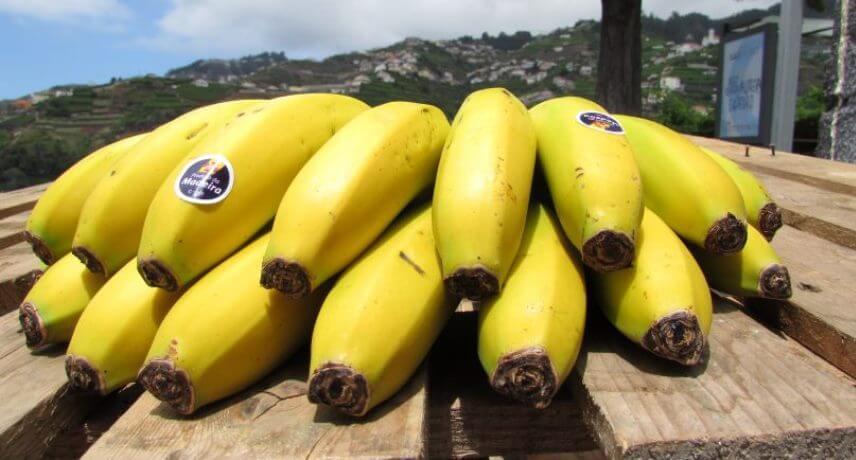

Banana was first introduced to the Madeira archipelago in the 16th century. This banana would be different from what we see today, and over time we have had the presence of different types of banana. The one we are most aware of today is the subspecies Musa cavendishii. There are other banana varieties available on the island, the silver banana and the apple banana, but their production is small and local, limited to personal gardens or small plots, so it is not easy to sell.
The banana from Madeira is characterized by its fruity and naturally sweet flavor, which contrasts with the majority of bananas available on the national market, usually from South and Central America. They are generally smaller, but their natural sugar content is higher and this is reflected in the flavor.
The banana grows easily on the island of Madeira due to its geographical position and the climatic conditions present on the island. The production takes between 12 to 14 months, from the plant's growth to the cutting of the banana bunch (usually one per banana tree). Most of the production is made in the south, between sea level and the elevation of two hundred meters, where there is high temperature, good sun exposure and water in abundance, coming from the north of the island through levadas. There are banana trees all over the south coast of the island, but there is a special focus on the Ponta do Sol and Calheta areas.
Banana is a fruit rich in vitamin A, vitamin C, fiber, iron, phosphorus, calcium, potassium and naturally present sugars. It has benefits for the immune system (due to the presence of vitamins A and C), for the maintenance and recovery of muscle mass (potassium in large quantities, which also makes it a more radioactive fruit than the rest), for the maintenance of bone density (due to the calcium present) and even contributes to weight loss (by having a high satiety factor). It is a food widely consumed by athletes and active people in general for providing energy, about 90 kcal per banana.
In the archipelago the banana is widely used in sweets, puddings, in the making of cakes, liqueurs or even as an accompaniment to fish dishes (see the traditional black scabbard fish with banana).
Tabaibo or prickly pear
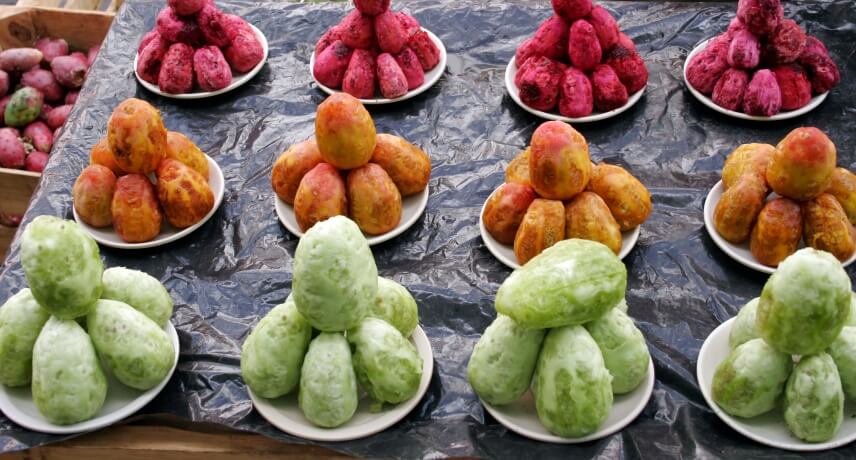

Tabaibo (Opuntia fícus-indica) is an oval, spiny fruit from the tabaibeira or fig tree, a plant of the cactus family. Most tabaibeiras grow spontaneously, not being cultivated for that purpose.
Tabaibeiras are thought to have been introduced to Madeira in the 19th century, coming from Mexico, where they abound. The purpose of this introduction was to produce the carmine pigment through small insects that are used to extract it.
This plant does well in warmer and even arid climates, which is why it is common throughout the South coast of Madeira Island, with special emphasis on Fajã da Ovelha, where there is even a small festival dedicated to this fruit and Caniço, and also in Porto Santo. There is no organized production, it happens spontaneously. These fruits are harvested between July and October and this must be done with gloves due to the natural spines of the fruit, which are small and cause pain and irritation if caught with unprotected hands.
There are several varieties of tabaibo distinguished by the color of the pulp, which can be white (the most frequent), orange or red.
In nutritional terms, this fruit is low in calories (about 42 kcal per 100g), with a high content of vitamin C, calcium, magnesium and potassium. The presence of vitamin C contributes to a strong immune system and has antioxidant properties. The calcium present in tabaibo has desirable effects on bone density and magnesium is important for reducing tiredness and fatigue. The potassium present in this fruit helps to control blood pressure and fluid retention. it is a fruit very rich in dietary fiber due to the abundant presence of seeds, which contributes to the regulation of intestinal transit, as long as it is not eaten in excess (due to having too many seeds, excessive consumption can result in constipation in particularly sensitive people).
Tabaibos are a summer fruit and therefore the ideal is to consume them fresh, coming directly from the refrigerator. Some also use them for liqueurs and jams.
Grapes
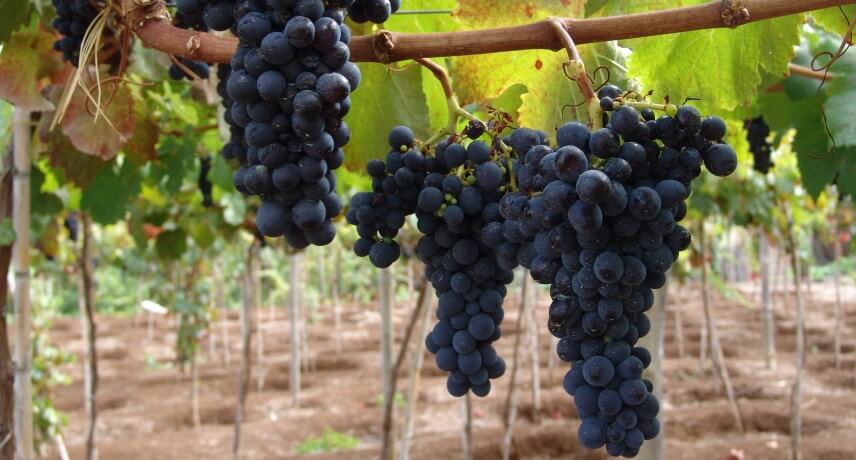

The grape is an inseparable fruit of the archipelago's own history. Its introduction practically dates back to the beginning of the island's population. The first grape varieties are said to have also been introduced by Infante Dom Henrique. The grape is obviously linked to the production of Madeira wine.
The mild climate observed throughout the year on the island and the fertile soils have greatly contributed to the establishment of grape cultivation on the island and for the purpose of wine production. Madeira Wine has played an important role in the island's economy over the years, becoming a popular and quality product all over the world. As a curiosity, Madeira Wine was present in 1776 at the independence of the United States of America, being the favorite wine of Thomas Jefferson.
The grapes most produced on the island are those of Tinta Negra, Sercial, Boal, Verdelho and Malvasia. Tinta Negra is the most produced, its culture is in the south of the island, in Funchal and Câmara de Lobos and in the north, in São Vicente. Sercial, very acidic, is produced in the north of the island and in Câmara de Lobos. Verdelho is generally grown at 400 meters above sea level. Boal is produced between 100 to 300 meters and is more present in Campanário and São Vicente. The Malvasia grape variety, which is believed to have been the first to be introduced to the island, is mostly found on the north coast of the island.
It is also worth mentioning the production, albeit in a very small quantity of white grapes in Porto Santo, sweet and light grapes that are rarely seen outside the island of Porto Santo.
The harvests traditionally take place at the end of August and the beginning of September, and from 3 to 27 September there is the Wine Festival, which is one of the tourist posters of the destination Madeira. It is also worth mentioning the Grape and Farmer Festival that takes place in Porto da Cruz practically simultaneously.
The vast majority of grapes produced in the archipelago are for the production of wine, although some are also available for sale in traditional markets. it is worth noting that although it is an alcoholic beverage, when consumed in moderation wine presents health benefits, such as the effects of lowering blood pressure or even anti-inflammatory effects. The grapes themselves have a high degree of satiety, being rich in antioxidants and vitamins C and K, and also in flavonoids, which help in reducing the so-called bad cholesterol.
Delicious Fruit
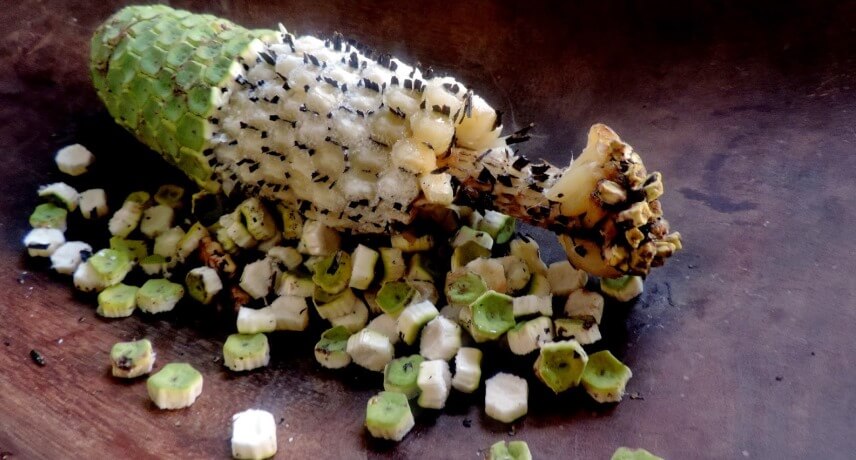

The Delicious Fruit (Monstera delicious) is a long fruit with an exotic and fruity flavor, a mixture of banana, pineapple and anona. This fruit is originally from Mexico and the plant that originates it is a vine. The ideal for its production are the slightly higher temperatures in the south of the island, where it grows freely in private gardens, mainly in an ornamental way (its large green leaves are considered very beautiful). There is no large-scale production on the island.
It is a fruit that should be eaten as it ripens, since it does not ripen all at the same rate. It is very popular with visitors to the island because it is an unusual tropical fruit with a delicate flavor and peculiar shape. When ripe it is very pleasant, but when green it is toxic and therefore care is advisable. This fruit is very low in calories, has a high content of potassium and vitamin C.
Physalis
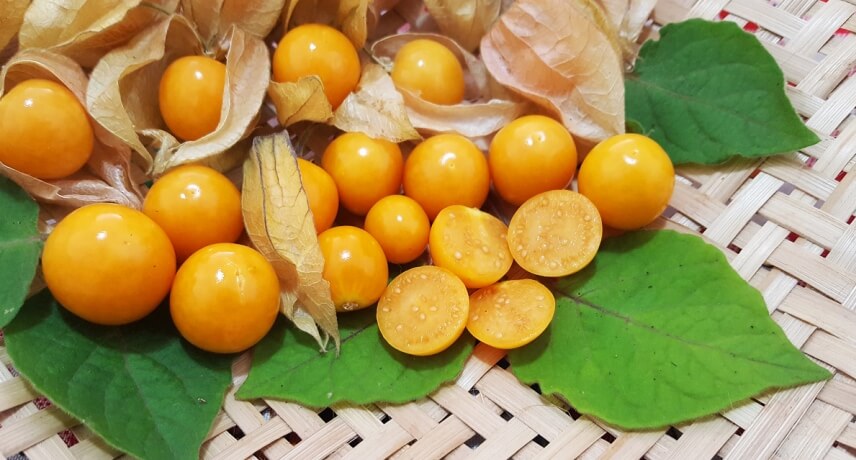

Physalis is a tropical fruit originally from South America. Scientifically named Phisalys peruviana L., this is an invasive plant that grows spontaneously without the need for great care. The plant grows well especially on the south coast of Madeira Island. The fruit is round and has a sweet and sour taste. From the point of view of health, the fruits have antioxidant properties (preventing the formation of free radicals in the body) and anti-inflammatory properties, given the presence of physalin, pointed out as a weapon against cancer and tuberculosis in some studies. The fruits are also colloquially recommended for those who have skin diseases. They are rich in vitamins A and C and fibers that help to regulate blood sugar levels.
Physalis is widely used in jams and jellies, and is also eaten by itself.
Tamarillo or English Tomato
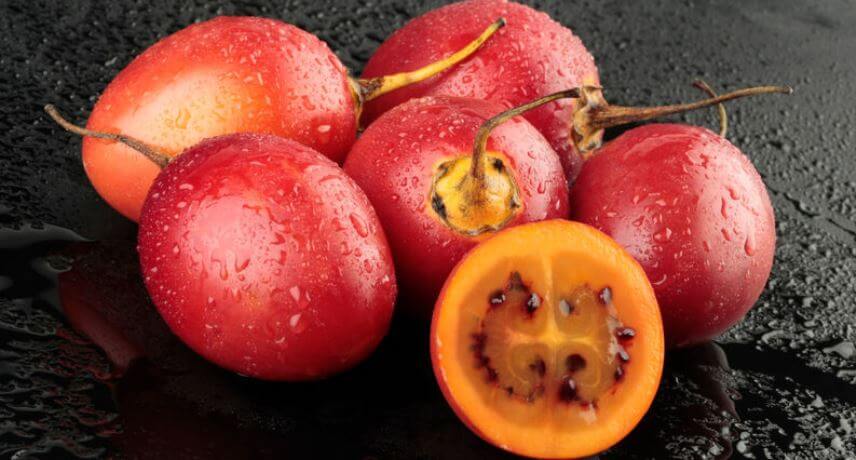

The English tomato or tamarillo is a fruit of a plant originally from the Andes. On Madeira Island we can find them everywhere, from an altitude of 300 meters on the north coast and an altitude of 400 meters on the south coast. The majority of production, however, is concentrated in small plantations in the municipalities of Santana (Arco de São Jorge, São Jorge and Santana) and Santa Cruz (Camacha).
As the name implies, the fruit has similarities to tomatoes, being oval, red and a little pointed. The flavor, when properly ripe, is both sweet and acidic and can be eaten by the spoon naturally or integrated into salads, jams or even liqueurs and poncha.
This fruit is rich in antioxidants, which helps in strengthening the immune system and low in calories, so it can be eaten freely even by those who have to be careful with their diet!
Chestnut
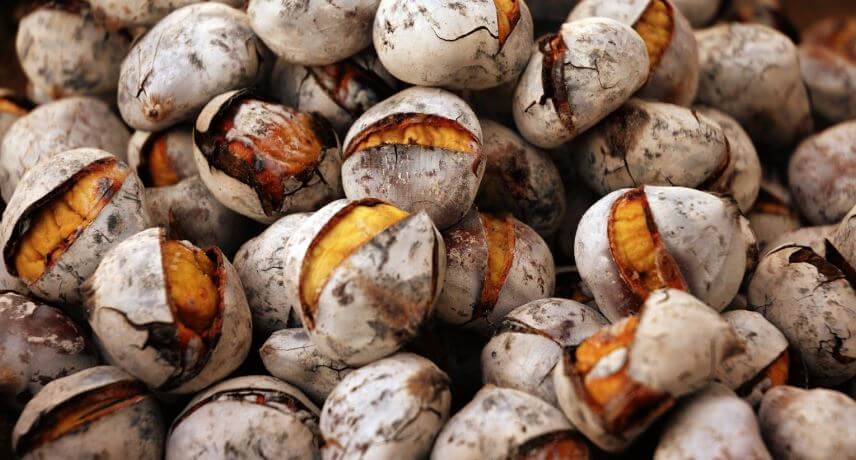

The chestnut (Castanea sativa) is an ancient fruit consumed in Europe for over 3 thousand years. It is believed to be from Asia. In reality the nut is technically a seed and not a fruit. Most likely, the chestnut tree was introduced as early as the island's first settlement, in the 15th century.
The main production of chestnuts is concentrated in the parishes of Jardim da Serra, Curral das Freiras and Serra de Água, at altitudes ranging between 400 and 1000 meters.
The chestnut even plays a central role in the parish of Curral das Freiras, where the Chestnut Festival has been held for three decades, very popular with Madeirans and visitors and which usually takes place on the 1st of November. At this party we can indulge ourselves with roasted chestnuts, very typical of autumn throughout the national territory, with chestnut jams, with typical dishes, liqueurs and even food flours based on this versatile fruit.
Chestnuts are very rich in carbohydrates, however they are low in fat and calories. They are rich in folate and vitamins C and B6, and are good sources of riboflavin and thiamine. The fibers present are very beneficial for the intestines, stimulating the presence of important probiotic bacteria. It also contains important minerals such as calcium, iron, magnesium, potassium, phosphorus, zinc, copper, manganese and selenium.
Therefore, chestnuts are ideal for those suffering from gluten sensitivity, being able to substitute certain cereals rich in this protein and fill energy needs.
Avocado
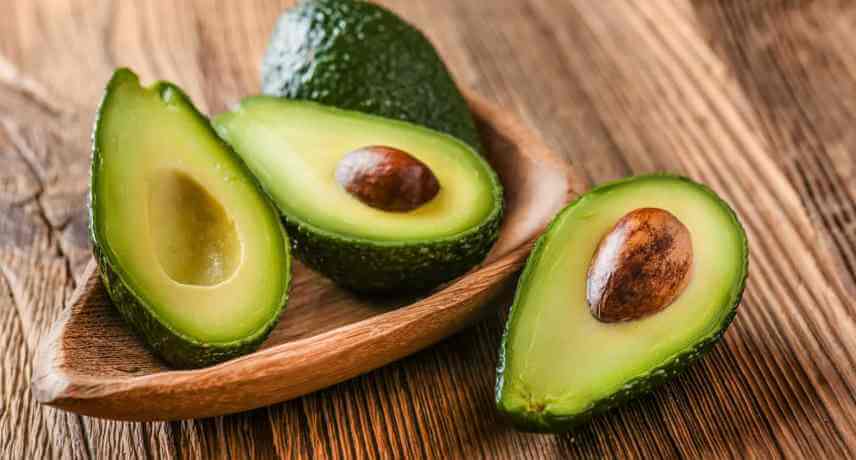

The avocado tree, the avocado (Persea americana Mill.) was introduced to the archipelago of Madeira sometime in the early 19th century, by a morgado returning from Brazil. The origin of the fruit is clearly much older than that, the fruit originates from Mexico, Guatemala and the Antilles and there is evidence of its consumption in Central America that goes back 10,000 years.
Here in Madeira it is known as Avocado or Pear-Avocado, because it reminds us of a pear format.
Avocados can be produced up to 400 meters on the south coast and 150 meters on the north coast of the island. Most of the production is in Santana, Funchal, Santa Cruz and Calheta. A lot of the population has avocado trees on their small plots or gardens, it is a plant that has adapted well to the island. Island production has grown sustainably in recent years.
The two most commercialized varieties are "Hass" (with rougher, darker skin) and "Fuerte" (with smooth, pear-shaped fruit). The typical season is from October to July.
In terms of flavor the avocado has an extremely smooth and buttery texture, an equally delicate flavor. It is a popular fruit these days and can be used in sweet and savory dishes, in salads, with fish, with eggs or even by itself or as some Madeirans like to consume with a little sugar on top (something somewhat controversial for some!). In nutritional terms, this fruit has 162 kcal per 100g, making it a very caloric fruit. Despite this, it is very nutritious, being a source of potassium, folate and vitamin A, rich in vitamin E and vitamins B6, C, iron and magnesium. It has a high content of monounsaturated fatty acids that are linked to the reduction of cholesterol levels in the blood.
Papaya
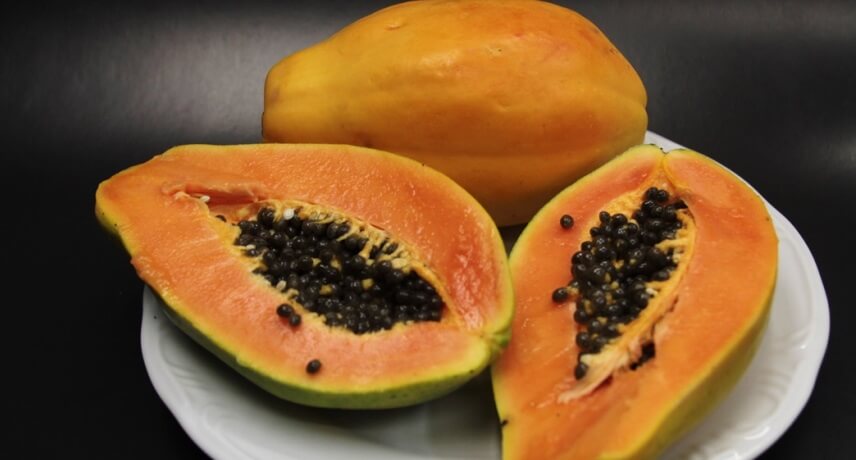

Papaya is a tropical fruit of papaya. it is possible to see papayas fruiting throughout the year, but in summer the frequency is higher. Production is generally done up to 250 meters on the south coast, in scattered feet and in small plantations.
The papaya (Carica papaya) is originally from Central America and North of South America. It is a sweet fruit with a soft pulp full of round black seeds that are removed before consumption. Because it has a very pleasant and tropical flavor it has become very popular and local production has proved to be of great quality, and often the fruits of small local farmers far exceed the quality of imported fruits that we often find in supermarkets. The production on the island focuses mainly on small farmers, and it is most successful in the Ponta do Sol Municipality.
Papaya is a very versatile fruit, and can be consumed naturally, in juices, smoothies, puddings, jams or even liqueurs. Regarding the nutritional value of papaya, this is obvious: it is abundant in vitamin C, A, calcium, phosphorus, iron, sodium and beta-carotene. This nutritional profile favors the strengthening of the immune system, intestinal health (since the presence of soluble fiber promotes a certain laxative effect) and even in the control of cholesterol.
Watermelon from Porto Santo
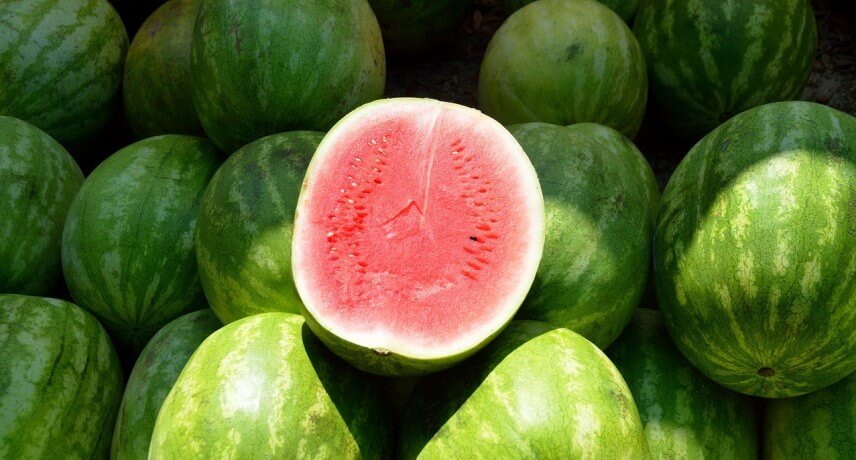

Watermelon (Citrullus lanatus) is a fruit that is typically seen on Porto Santo Island during the peak of summer, when, in fact, there is the Watermelon festival itself (at the end of August).
It is not clear when the fruit was introduced in Ilha Dourada, but the truth is that it has become one of the products most associated with Porto Santo. This plant was originally domesticated in Africa and later cultivated and spread around the world from Egypt. It is a crop given at higher temperatures and drier climates, hence it does well in Porto Santo.
It is a fruit rich in water and very low in calories, about 30 kcal per 100g. Contains vitamin A, B vitamins, vitamin C, lycopene and folic acid. It is an advisable fruit for those who have difficulties in hydrating and for those who have urinary problems.
Fig
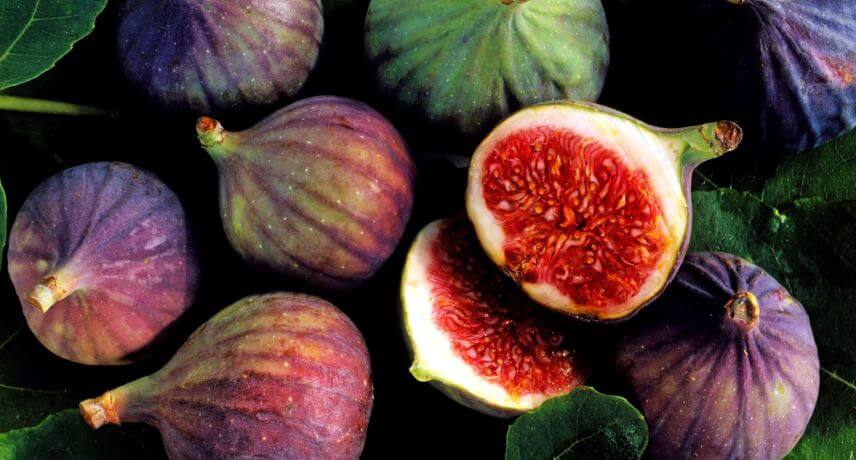

The fig (Ficus carica L.) is a small and sweet fruit originally from Southwest Asia, being found in the European Mediterranean countries and in North Africa. Figs have been present in the human diet for thousands of years, being one of the first species to be cultivated. It is a very relevant fruit in the Mediterranean diet, especially in the area of influence of the Middle East.
On the island of Madeira, the date of its introduction is unknown, however it is possible to see fig trees all over the archipelago. It is common to see fig trees especially on the south coast of Madeira from the coast up to 400 meters in altitude. There are also fig trees in Porto Santo. It is a plant easily adaptable to various climatic conditions and is usually ready to be harvested between July and September.
In Madeira it is possible to find some varieties of fig, among which, Pingo Mel, Bebera Branca, Bebera Preta and Cotios.
The fig is a fruit that contains potassium, calcium, phosphorus, vitamins A, B1, C and K and plenty of dietary fiber, so it is recommended for those suffering from intestinal disorders such as constipation.
It is common to find dried figs in jams and chutneys or even in liqueurs.
Porto Santo "Table" Grapes
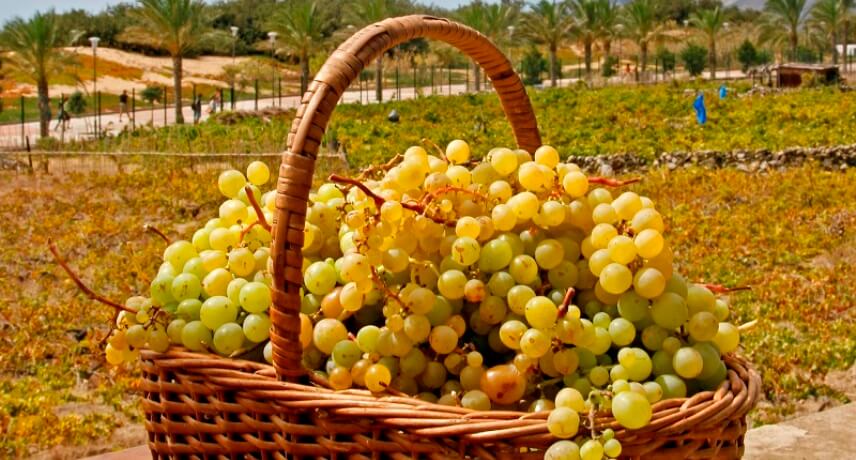

Table grapes are a typical fruit of the island of Porto Santo, not found outside this island. Belonging to an almost endangered variety, Listrão, in the past, were used in the production of Madeira wine, as the grapes were sweeter and helped to attenuate the low grade of Madeira wines. Nowadays the production of this grape is local and done by only a few farmers on a residual basis. We can see them being sold by small fruit stands on the island of Porto Santo, but not outside it.
These sweet grapes are still used for the production of table wine by some local traders, being possible to taste it in restaurants like 3 V’s in Vila Baleira. Grapes are also used to make wine jelly, grape jam and jams, in addition to the seed that is used to make flour, bread, breads and chocolates.
Ponta do Pargo Apple
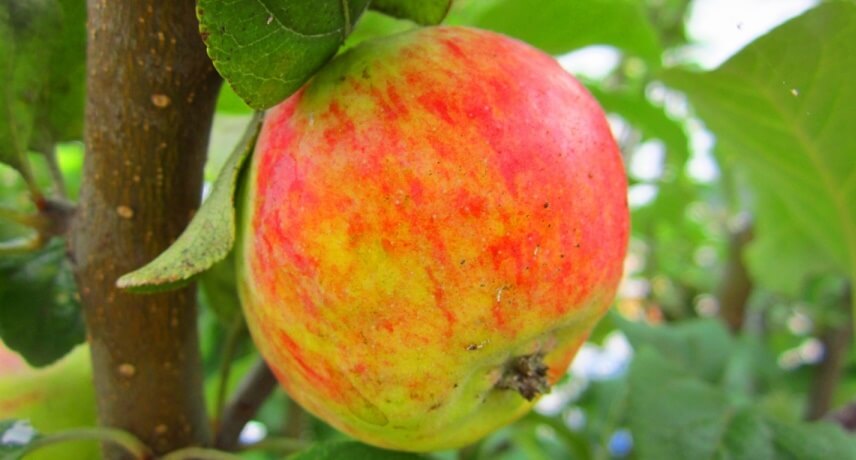

The apple that is traditionally produced in Ponta do Pargo is nothing more than a small apple with a very characteristic and acid flavor. The typical apples in this town are usually small and are usually harvested between the end of August and September. There is an annual festival dedicated to this fruit in this parish that happens in September.
This is a very delicate fruit, it tends to be “hurt” in transport.
The apple of Ponta do Pargo, because it is very acidic, is not a natural fruit to eat. Usually this type of apple is cooked or baked in the oven with a good dose of sugar, in order to balance the natural acidity. Often they are also used to make cider.
The apple is naturally low in sugar, rich in fiber and abundant in vitamin C, combined with a strong immune system.
Lemon
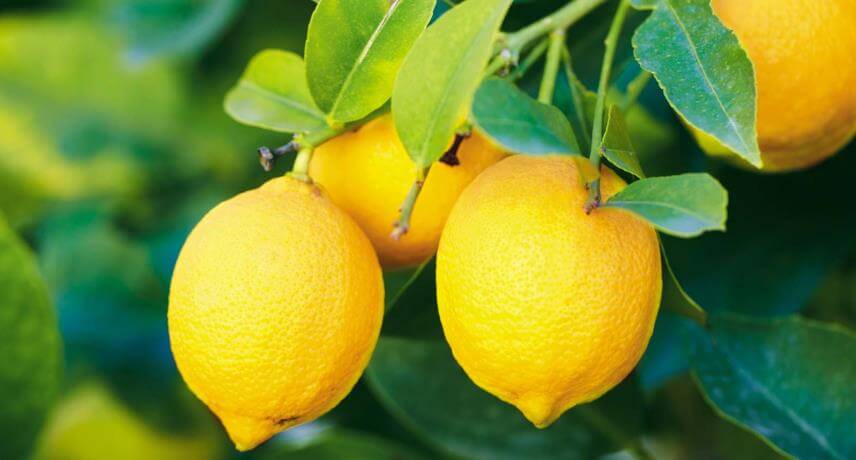

The lemon (Citrus limon) is a small, acidic oval shaped citrus, usually yellow or green in color. The lemon is thought to originate in northern India, on the current border with China and Burma. It will have entered the European continent through the region of Italy at the time of the Roman Empire. It was also spread across the territories of the Middle East and North Africa, gradually becoming a central element in the gastronomy of these peoples.
There are many varieties of this fruit, however the most used are lemon, lemon, clove and lemon-tahiti.
The lemon is a fruit very low in calories (about 29 kcal per 100g), but rich in vitamins and minerals important for the functioning of the body. This fruit has a high content of vitamin C, important for the immune system and that increases the absorption of iron, contributing to the reduction of tiredness and fatigue. it is a fruit with antioxidant capacity due to the presence of vitamin E, vitamins of the B complex, namely B1, B2 and B3. Lemon also contains pectin in your skin, an element that helps to reduce LDL cholesterol levels in your blood. Also in the lemon peel we find d-limonene, which has antiseptic and antibacterial effects, and has a diuretic effect, which helps to prevent fluid retention.
The lemon is produced in greater quantity in the parish of Ilha, in Santana. In this locality, about 90 tons of lemon are produced annually. Every year there is a party dedicated to this fruit, in which local producers display their products, and in which the most varied products and sweets made from lemon are sold.
The lemon is a very versatile fruit, being used to make jams (as a main element or as one of the secondary ingredients), a wide variety of cakes, puddings and mousses, in juices, poncha, in liqueurs, as a spice in cooking ( from salads to meat and fish dishes), among others.
Cherries
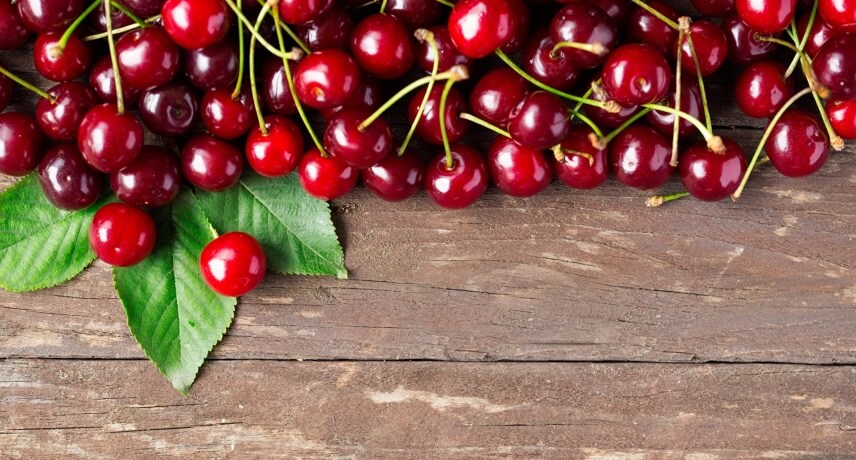

The cherry is a small round and usually red fruit. This originates from the region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea.
On the island of Madeira the cherry trees are essentially above 500 meters on the south coast and 350 meters on the north coast, as it needs colder and less tropical climatic conditions. The main areas of cherry production in Madeira are Jardim da Serra, Serra de Água and Curral das Freiras, and the cherry blossom party is in Jardim da Serra. The Madeiran cherry is a little smaller than the cherry originating in mainland Portugal that we can usually see in most supermarkets.
It is a fruit whose harvest is made between the months of May and June, making it a typical fruit from the beginning of summer.
The cherry has a low energy content and a lot of fiber, which makes it a satiating food. It is a fruit rich in potassium, vitamin A and vitamin C, properties that assist in the elimination of toxins and liquids from the system.
Cherries are eaten naturally (must be kept cold), used to make cakes, pies, sweets or even liqueurs.
Loquats
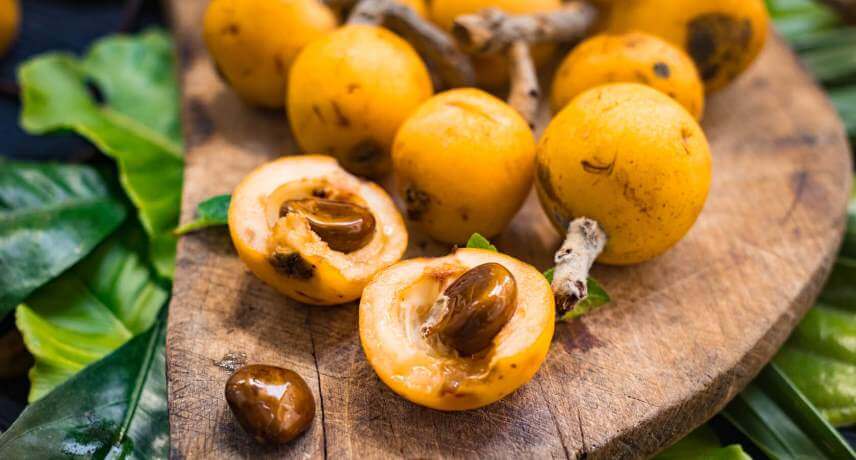

The loquats are a small fruit originally from Asia and introduced in Madeira in 1846. This fruit has a yellow or orange color and seeds relatively large for their size. Its taste is sweet, but with a good dose of acidity.
Loquats are grown all over the south coast of Madeira, with a higher prevalence of trees of this fruit in the area of Machico.
Loquats are a fruit with low energy content (45 kcal per 100 g) and have a high percentage of water, being very moisturizing. They are rich in beta-carotene, fiber, potassium and vitamin A, which makes them a good ally of the circulatory system, namely the heart. The presence of these vitamins also helps to prevent free radical damage in cells.
In Madeira they're are usually consumed natural and used in the production of liquors (such as those made from the pits).
Araçal
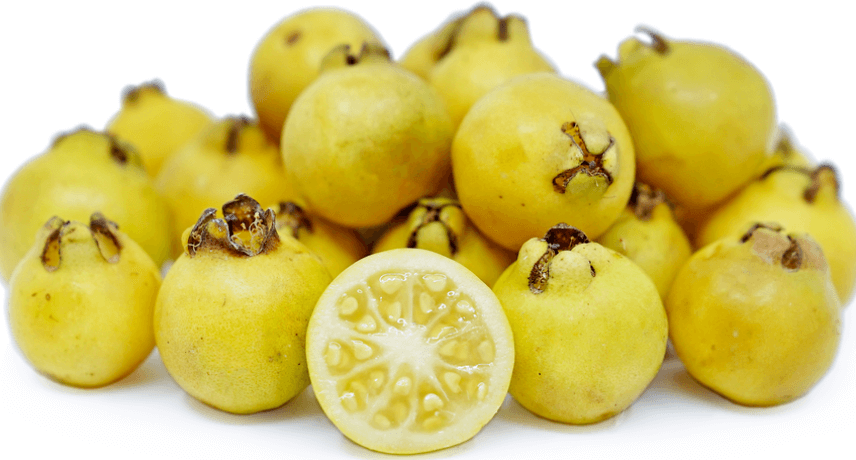

The araçal (Psidium cattleyanum) is a small, rounded yellow fruit originally from Brazil. It is common to see araçaleiros all over the south coast of Madeira Island, as it is a plant that needs a tropical climate and a lot of light.
Araça is a tropical fruit with a flavor similar to guava, but with a little more acidity and a whitish pulp with small seeds.
This fruit is extremely rich in vitamin C, its consumption promotes a strong immune system. It also contains calcium, phosphorus and iron, having anti-inflammatory effects.
The araçal is a typical fruit of the peak of summer, especially between August and September. It is common to see araçaleiros in private gardens as it is a plant that is easy to grow, without the need for great care.
In Madeira, araçais are eaten by themselves or integrated in jams.
Tangerine
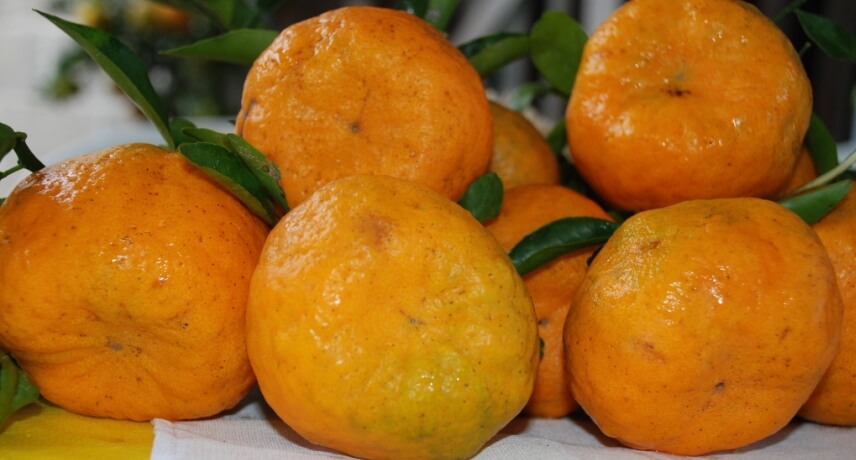

Tangerine (Citrus reticulata Blanco) is a small orange spherical citrus fruit very typical of the Madeiran Christmas period (although it can be found at other times of the year as well). The tangerine has a very strong aroma and a sweet flavor, it is common to see them decorating the traditional lapinha of Madeiran Christmas.
Tangerine is grown throughout the region, but there is a greater incidence in the municipalities of Funchal, Santa Cruz, Câmara de Lobos and Ribeira Brava. In Santa Cruz, there is even an annual party dedicated to tangerines.
This fruit is low in calories (53 kcal per 100g) and is rich in fiber, vitamin C and potassium. It has antioxidant effects through nobiletine that controls and prevents the elevation of cholesterol, thus preventing cardiovascular diseases, such as arteriosclerosis and stroke.
In Madeira it is traditional to eat tangerines at Christmas, but they are also used in sweets and in liqueurs and poncha.
Plum
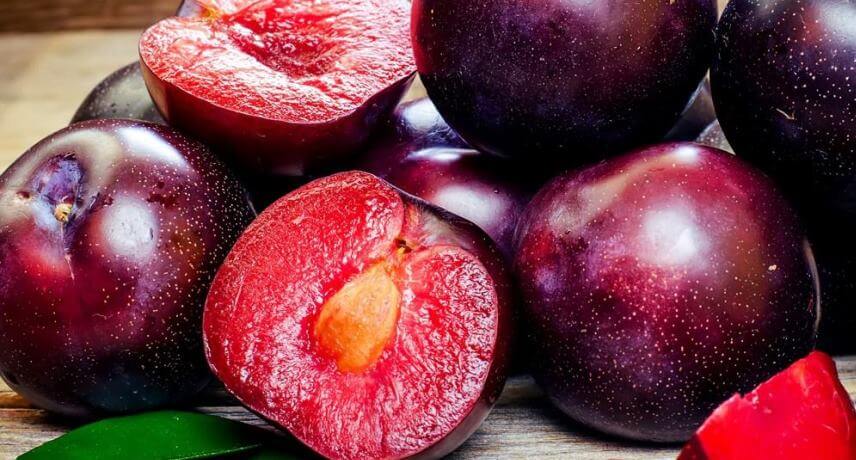

Plum has its origin in the Caucasus, Anatolia and Persia. On the island of Madeira, plum is mainly grown in Santo da Serra, Jardim da Serra, Curral das Freiras and Camacha.
It is a typical summer fruit, harvested between June and September. Plum is a round fruit with some color variation, from dark purple to light green. Its flavor also varies from the sweetest to the most acidic.
Plum is abundant in vitamin C, A, beta-carotene, potassium, iron and antioxidants. Its fiber content is a strong ally of intestinal health.
Mango
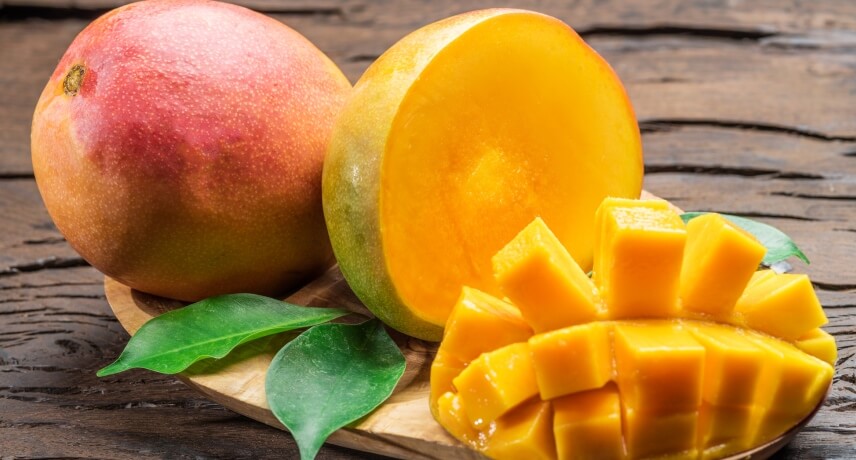

Mango is a tropical fruit originally from India. There are several varieties of mango, but they have a sweet and fruity flavor and a soft, sometimes fibrous pulp with a central core. Mango trees are more present on the south coast of the island, from the coast to 180 meters in altitude and in the north, in sunny fajãs up to 50 meters in altitude.
The mango has a varied color, from yellow, orange to red.
This fruit is abundant in fiber (which enhances intestinal health), iron (suitable for anemia sufferers), potassium and magnesium.
it is often consumed fresh or in juices, milkshakes, puddings, yoghurts, sweets, among others.
Banana Passion fruit
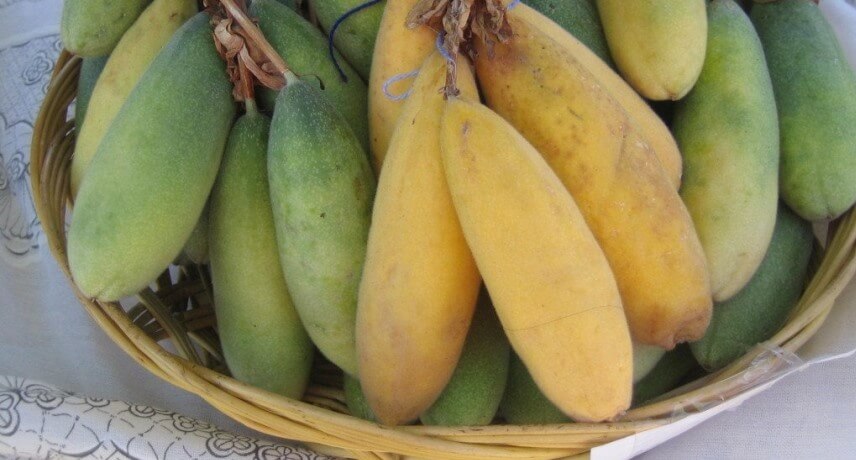

The passion fruit banana is a fruit from the highlands of Venezuela to Bolivia and with an elongated and yellowish aspect, hence the name related to the banana. It appears sporadically on Madeira Island and is characterized by a flavor close to the purple passion fruit, but with less acidity and less juice. It is a fruit that is produced in high areas and tolerates lower temperatures well.
It is a fruit rich in calcium, iron, niacin, riboflavin, sodium, vitamins A and C. In Madeira it is normally consumed naturally, and can also be integrated in juices and other sweets.

